Storms are becoming more intense as the climate changes. This is just one reason why the signing of the Paris Agreement by 170 nations in New York last week is great news. Finally, there is a sense of momentum; a shared purpose worldwide that the rate of climate change urgently needs to be slowed down. The next—and most important—step is for countries to ratify the treaty and enshrine the agreement in national legislation. Let’s all hope this progresses smoothly and quickly.
This collective enthusiasm to reduce humanity’s greenhouse gas emissions cannot come fast enough. The first three months of this year have been record-breakers in terms of global temperature, causing heatwaves, extensive coral bleaching, and continued declines in the Arctic sea ice.
Implications of climate change on rainfall intensity
Potentially equally important to these direct effects of increasing temperature are the indirect effects of greenhouse gas emissions on the world’s weather patterns. And of these, changes to extreme storms are particularly important. Alarmingly, the evidence is suggesting that storms have started becoming much more intense.
The basic logic is that a warmer atmosphere can hold more water. If this seems unexpected, then consider why we use warm air for hand-driers, or why on warm humid days you can get water droplets forming on the outside of cold water bottles. Or why storms in the tropics are often much more intense than those in the higher latitudes.
Because of this, we have good reason to expect that storms should become more intense as the climate warms. In fact, scientists who have looked into this expect the rainfall intensity from storms to increase by between 7% and 14% for every degree of global temperature increase.
This is not just some theoretical concept about what scientists expect in the future; it’s something we’ve already started to observe. Don’t believe me? Well then, you can read more here, here, here, here, here and here.
The changing size of storms
But is a change in the intensity of storms the only thing we can expect? This was the question we asked when I began collaborating with PhD student Conrad Wasko and his supervisor Professor Ashish Sharma at the University of New South Wales. Here, we did a comprehensive analysis of data from 1300 rain gauges and 1700 temperature stations across Australia to see how air temperature affects the spatial organisation of storms.
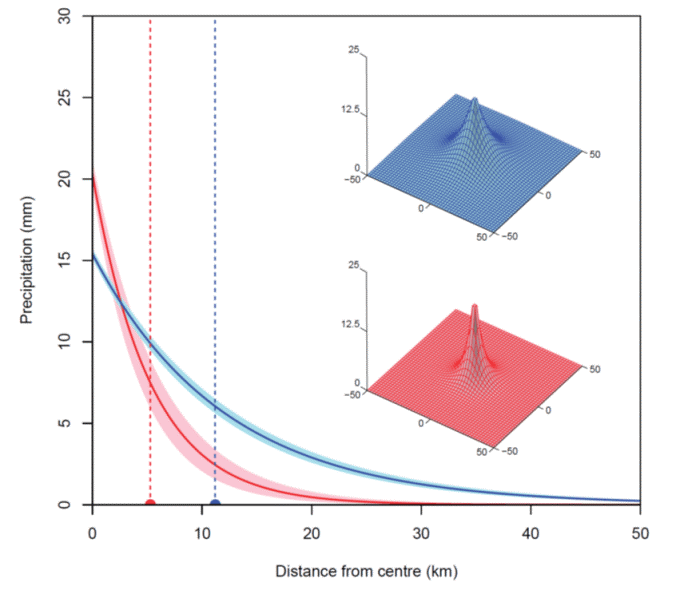
What we found was surprising: not only do storms intensify with temperature, but they also become more concentrated over a smaller area. This is because as the storm cells intensify, they also become more effective at drawing in moisture toward the storm centre.
This is illustrated in the image below, where we looked at the 1000 most intense storms that occurred when the atmosphere was relatively cool (about 18 degrees Celsius or below, shown as the blue curves), and compared them to 1000 most intense storms when the atmosphere was relatively warm (above 25 degrees Celsius).
But what was really surprising was how uniform the changes were around Australia. In fact, regardless of whether we were looking at storms in temperate Tasmania or the tropical north of Australia, the humid east coast or the arid interior, the results were pretty much the same. A warmer atmosphere is associated with more intense rainfall, occurring over a smaller geographic area.
If we combine this with the large number of other studies that have recently been published on changes to extreme rainfall under climate change, it is clear that we are beginning to have a much better understanding of these changes. But there is still much to learn about what climate change will mean for changes in storms, and how this is related to possible changes in flooding, hail damage and other meteorological hazards.
Nevertheless, the sorts of changes our team and others around the world have been documenting are cause for concern. So let’s hope that Australia starts following the chorus of international support for stronger action of climate change and takes the action needed to ratify the Paris Agreement as soon as possible.
Further reading
There are literally hundreds of scientific papers that have been published describing historical and expected future changes in extreme rainfall. I’ve provided a selection of papers from our own group on the topic below. The first paper provides a review of nearly 250 scientific papers on the topic, and can be used as an entry point to the broader literature.
- A review of the international literature: Westra S, Fowler HJ, Evans JP, Alexander LV, Berg P, Johnson F, Kendon EJ, Lenderink G, Roberts NM, 2014, Future changes to the intensity and frequency of short-duration extreme rainfall, Reviews of Geophysics, 52, 3, 522-555.
- The discovery that extreme rainfall intensity increases with atmospheric temperature: Hardwick-Jones R, Westra S, Sharma A, 2010, Observed relationships between extreme sub-daily precipitation, surface temperature, and relative humidity, Geophysical Research Letters, 37, L22805, 1-5
- Evidence that daily-scale extreme rainfall is increasing around the world: Westra S, Alexander L, Zwiers F, 2013, Global increasing trends in annual maximum daily precipitation, Journal of Climate, 26, 11, 3904-3918
- Evidence that shorter-duration (e.g. hourly) rainfall is increasing more quickly than longer duration rainfall: Westra S, Sisson S, 2011, Detection of non-stationarity in precipitation extremes using a max-stable process model, Journal of Hydrology, 406, 1-2, 119-128
- The surprising finding that it is possible to have opposing trends in summer and winter rainfall: Zheng F, Westra S, Leonard M, 2015, Opposing local precipitation extremes, Nature Climate Change, 5, 5, 389-390
- An evaluation of whether regional climate models are capable to reproduce the physical processes leading to extreme rainfall: Cortés-Hernández VE, Zheng F, Evans J, Lambert M, Sharma A, Westra S, 2015, Evaluating regional climate models for simulating sub-daily rainfall extremes, Climate Dynamics, 1-16
- The finding that the spatial extent of extreme rainfall decreases at higher temperatures: Wasko C, Sharma A, Westra S, 2016, Reduced spatial extent of extreme storms at higher temperatures, Geophysical Research Letters, doi: 10.1002/2016GL068509
Original article published on Intelligent Water Decisions website, 26th April 2016 (Link)