Don’t blame the Murray-Darling Basin Plan. It’s climate and economic change driving farmers out

For the thousand or so farmers in Canberra in the past week venting their anger at the federal government, it’s the Murray-Darling Basin Plan to blame for destroying their livelihoods and forcing them off the land.
We can’t comment directly on their claims about the basin plan. But our research, looking at the years 1991 to 2011, suggests little association between the amount of water extracted from the Murray-Darling river system for irrigation and total farmer numbers.
That’s not to say there aren’t fewer farms in the basin now than a decade ago – there are – but our analysis points to the more important drivers being the longer-term influences of changing climate, economics and demographics.
Indeed our study predicts another 0.5℃ increase in temperature by 2041 will halve the current number of farmers in the basin.
Hostility to water recovery
Over many decades state governments in Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria and South Australia licensed to farmers more entitlements to water than the river system could sustain. The basis of the Murray-Darling Basin Plan, enacted in 2012, was to rectify this through buying back about a quarter of all water licences to ensure an environmental flow.
A water entitlement, despite its name, does not guarantee a licence holder a certain amount of water. That depends on the water available, and that is determined by the states, which make allocations to each type of licence based on its type of security and current conditions.
With drought, farmers have seen their allocations severely cut back, sometimes to nothing. And partly because they see there’s still water in the River Murray, some are very angry.
Hostility to water recovery in fact predates the plan’s enactment, to when the federal government began buying back water entitlements in 2008. The Commonwealth now holds about 20% of water entitlements across the basin. More than two-thirds of these licences were recovered between 2008 and 2012.
Lack of correlation
Our research thus covers the period of most significant water buybacks. It also covers the period of the Millennium Drought, from 2001 to 2009, when the amount of water extracted from the river system dropped by about 70%.
Yet we see little evidence reduced water extractions led to more farmers exiting the industry.
As a very broad overview of the situation, the following graph illustrates the lack of correlation between measured water extraction in the Murray-Darling Basin and decreasing farmer numbers.
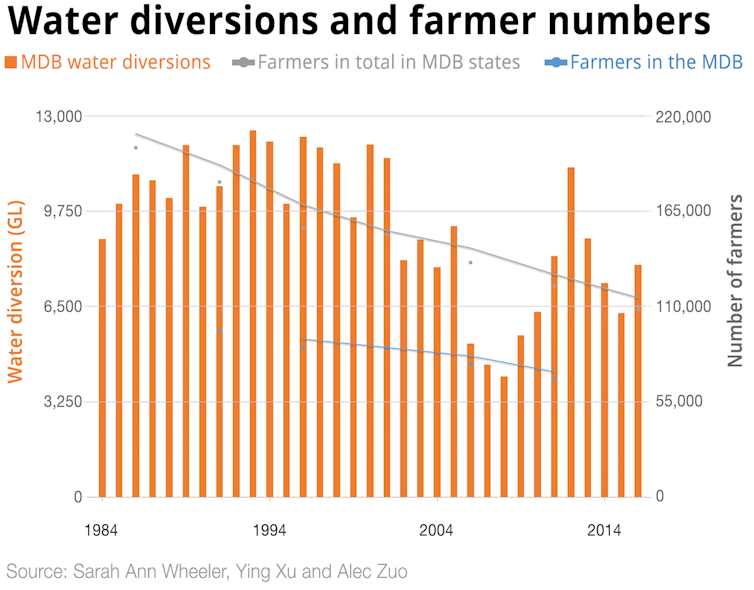
Water extractions have varied significantly between years, with a big decline over the decade of the 2000s even while farmers’ need for irrigated water increased due to lack of rain. La Niña brought record rains in 2010-11. The current drought across the basin took grip from about 2017.
Yet farmer numbers have declined at a relative steady rate. Within the basin in the time-period we modelled, they fell from about 90,000 in 1991 to 70,000 in 2011. This can be seen as part of a wider trend, with total farmer numbers in the four basin states falling from more than 230,000 in 1976 to barely 100,000 in 2016.
It might be argued that because irrigated farms make up only a quarter of all farms, the overall numbers might mask a greater correlation between water extractions and decline in irrigated farms. While the specific impacts on irrigation farming in recent years warrant further study, there’s no signal in our data pointing to extractions making a discernible contribution to farmer numbers throughout the basin.
Modelling farmer movement
Our findings are based on a specialised data set of population and agricultural census information from statistical local areas from 1991 to 2011. We used climate risk measures from 1961 onwards.
The infographic shows the exit pattern of farmers by local area between 1991 and 2011.
We included as many climate, economic, farming, water and socio-demographic characteristics as possible to capture historical farmer movements and create a model able to predict movements based on variables such as average temperature.
Need for a multifaceted response
Overall our modelling results suggests the most significant and largest influences on farmer exit are rising temperatures and increased drought risk, followed by the economic factors that have have been reducing the proportion of the population engaged in farming for more than a century.
Declining commodity prices, higher unemployment and urbanisation are strongly associated with farmer exit. Urbanisation, for example, has made it attractive for farmers on city fringes to sell their land to property developers and exit the industry.
Research suggests irrigators in psychological distress are more likely to want the basin plan suspended. Our research suggests their distress is probably not primarily driven by the federal government buying water entitlements from licence holders who sold them willingly. Water recovery and the basin plan is simply an easier focal point of blame than the longer-term trends making the farming lifestyle less viable.
Nothing will be gained by focusing on short-term “fixes” at the cost of longer-term environmental harm. The problems facing all farmers cannot be addressed in isolation from longer-term global climate and economic trends.
As a society we have to decide what we value: do we want to see such a mass exodus of farmers from the land in the face of a drying climate? If not, future policy for the Basin must consider the real long-term drivers of farm exit and take a multi-faceted approach to climate change, water, land, drought and rural development.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
